Simple Precision Time Protocol at Meta
Engineering at Meta
FEBRUARY 7, 2024
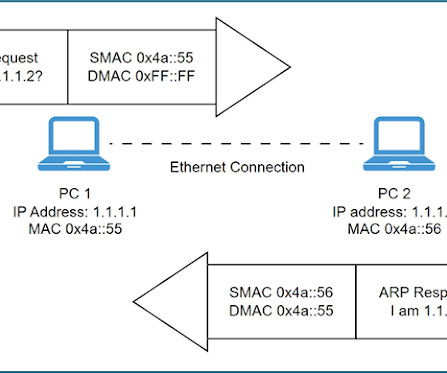
While deploying Precision Time Protocol (PTP) at Meta, we’ve developed a simplified version of the protocol (Simple Precision Time Protocol – SPTP), that can offer the same level of clock synchronization as unicast PTPv2 more reliably and with fewer resources. Complete trust in the validity of server timestamps.






Let's personalize your content