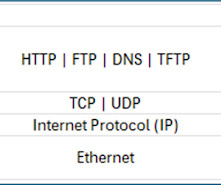
CCNA: TCP/IP Stack
The Network DNA
JUNE 4, 2024
It specifies how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, and routed across the network. TCP/IP stack has four layers Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Interface. The OSI Layer Data Link and Physical layer maps to the Network Interface layer of the TCP/IP stack.






Let's personalize your content