CCNA: TCP/IP Stack
The Network DNA
JUNE 4, 2024
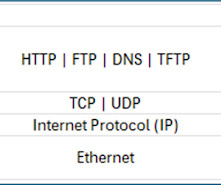
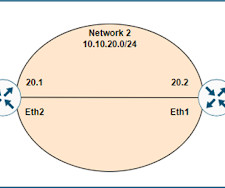
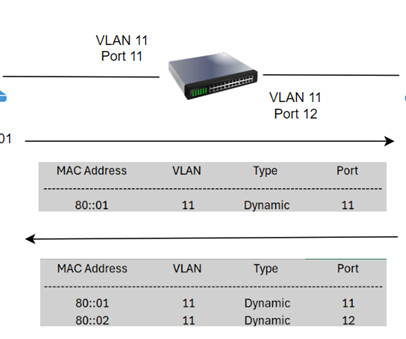
CCNA: TCP/IP Stack TCP/IP Stack is the most widely used protocol stack. TCP/IP stack is a conceptual model consisting of network communication protocols. TCP/IP stack has four layers Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Interface. TCP/IP networks use TCP or UDP protocol at this layer.








Let's personalize your content