Multi-Path TCP: revolutionizing connectivity, one path at a time
CloudFaire
JANUARY 3, 2025
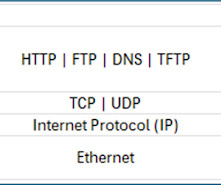
Enter Multi-Path TCP (MPTCP), which exploits the presence of multiple interfaces on a device, such as a mobile phone that has both Wi-Fi and cellular antennas, to achieve multi-path connectivity. It's a major extension to the TCP protocol, and historically most of the TCP changes failed to gain traction.






Let's personalize your content