23 Good-To-Know Networking Acronyms and Abbreviations
CATO Networks
AUGUST 17, 2021
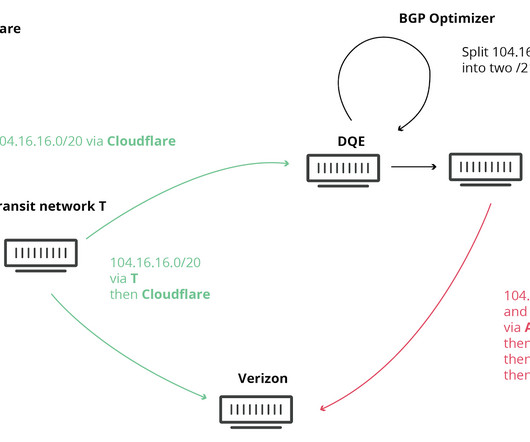
MPLS Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) routes traffic over telecommunications networks using short path labels instead of longer network addresses. BGP The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a protocol for exchanging routing information between different autonomous systems (ASes) on the Internet.






Let's personalize your content