AWS Route 53 BGP Hijack: What Kentik Saw
Kentik
MAY 2, 2018
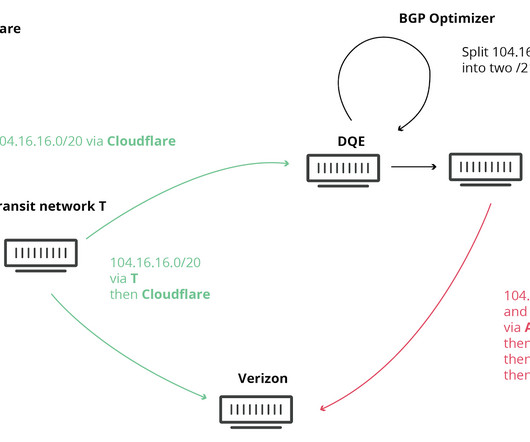
In simple terms, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the protocol that routes traffic on the Internet. During a BGP route hijack, an attacker advertises IP prefixes from an ASN that is not the normal originator. During last week’s attack, the attacker was redirecting traffic that belonged to Amazon’s Route 53 DNS servers.











Let's personalize your content